Psoriasis is one of the most common skin diseases.According to the International Federation of Psoriasis Associations (IFPA), it is detected in 125 million people worldwide.
In most cases, the disease develops in people of working age: from 15 to 35 years old.Men and women get sick with the same frequency.Despite the widespread prevalence of the disease, not all patients understand what psoriasis is, what are the causes of its appearance and how to treat it.Let's address all the questions in order.
Briefly about the main thing.
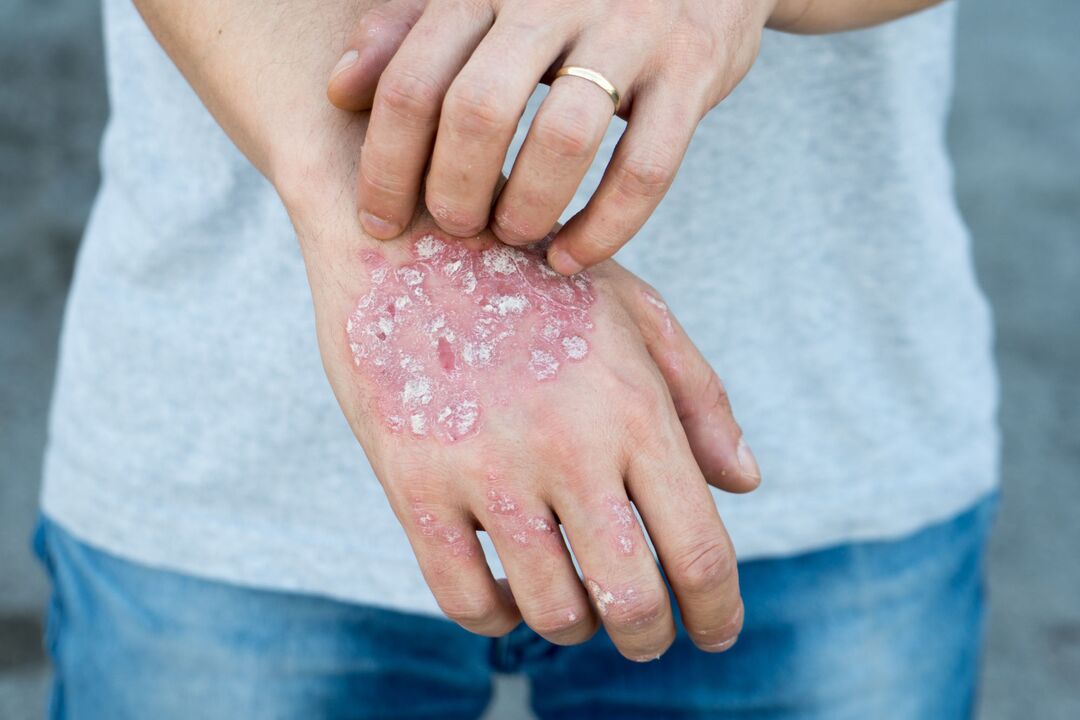
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease, characterized by the formation of specific “plaques” on the skin.The autoimmune mechanism is associated with the production of protective antibodies against the body's own cells, which it mistakenly perceives as foreign.Scientists have long established the connection between the disease and the activation of the immune system, but it has not yet been reliably clarified what exactly causes a failure in the recognition of one's own cells.
A genetic predisposition to psoriasis has been proven: if both parents are sick, the child has a 50% chance of also suffering from psoriasis.Some genes responsible for its development have even been identified.In addition, the influence of hormonal disorders, nervous tension, metabolic disorders and viral infections on the manifestation of psoriatic lesions of the body has been established.
Psoriasis in many cases is combined with diseases of other organs and systems:
- diabetes mellitus type 2;
- metabolic syndrome;
- pathology of the liver and biliary tract;
- coronary heart disease;
- arterial hypertension.
Classification and symptoms of psoriasis.
The main clinical manifestations of the disease depend on its form and course.
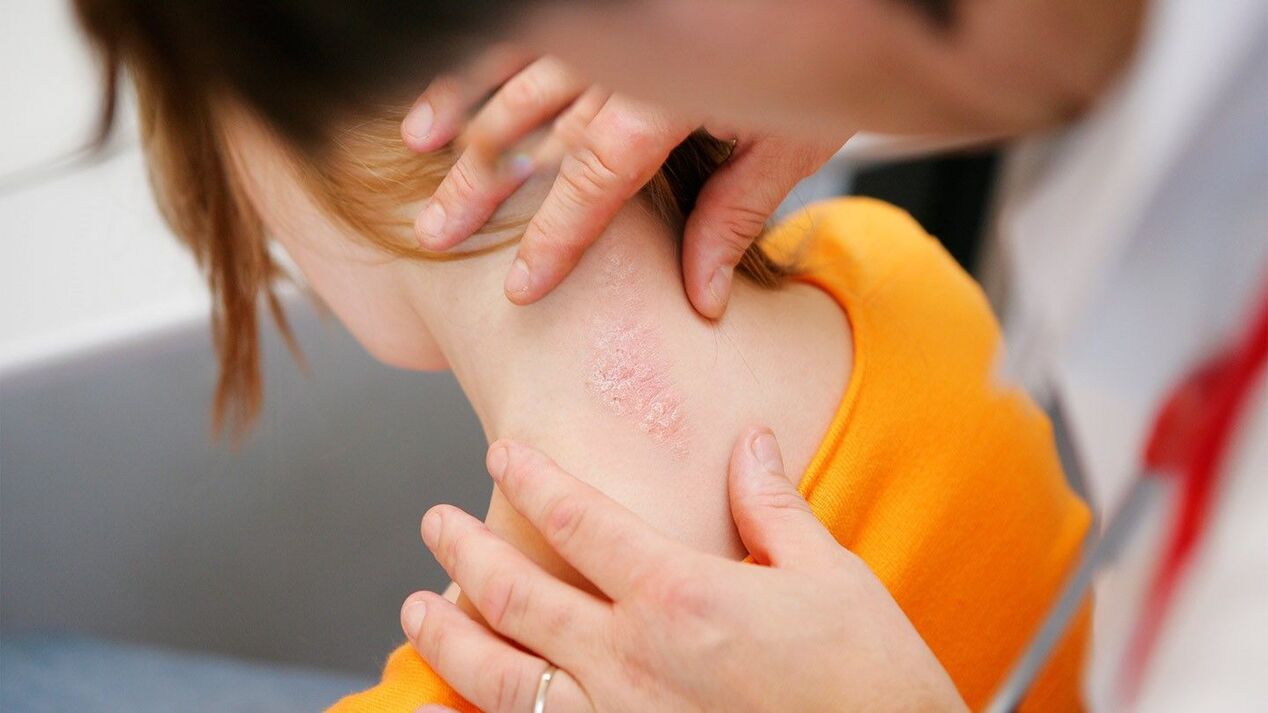
- Psoriasis vulgaris: characteristic rashes appear on the skin, which look like red, raised areas on its surface (so-called papules) with superficial peeling.Because of this, white scales appear, hence the second name of psoriasis - squamous lichen.If you scrape such an area, you can see the "stearin spot phenomenon" - the number of flakes will increase, resembling a frozen drop of stearin.After complete removal of the scales, a shiny, moist endplate is exposed, on which, upon further scraping, small individual drops of blood will appear.These papules are usually located on the scalp, on the extensor surfaces of the joints.
- Exudative psoriasis: an inflammatory fluid is secreted in the inflamed area that wets the scales, turning them into scabs that are difficult to remove.
- Seborrheic psoriasis is typical for areas of the skin with a large number of sebaceous glands: nasolabial folds, scalp, area between the shoulder blades and on the chest.In this variant, plaques with yellowish scales form that are very itchy.
- The teardrop shape is usually found in children and appears as multiple small red papules with slight scaling.
- Pustular psoriasis is a superficial pustule, usually located on the palms and soles of the feet.
- Generalized forms: psoriatic erythroderma, which is manifested by extensive confluent foci covering 90% of the body surface, and Tsumbusch psoriasis, accompanied by suppuration of extensive foci.With common forms of the disease, general well-being is also affected: weakness, malaise appears, and body temperature increases.
- Psoriatic arthritis is manifested by redness and swelling of the skin over the joints, pain, limited movement in the joints, their deformation and stiffness of movement after sleeping.
- Psoriatic onychodystrophy is a nail lesion.The “oil spot symptom” (yellowish-brown spots under the nail surface) and the “thimble symptom” (punctual damage to the nail) are characteristic.
How is psoriasis treated?

Methods for treating psoriasis are constantly being improved and supplemented, but there is no drug that can defeat the disease forever.Therefore, the main psoriasis treatment strategies are aimed at:
- reduction in the frequency of exacerbations;
- relief of symptoms of the disease;
- improve quality of life;
- reducing the likelihood of complications and concomitant diseases.
Treatment is usually done on an outpatient basis, but some conditions may require hospitalization:
- severe generalized variants of psoriasis, which worsen the general condition of the patient (in particular, erythroderma and pustular psoriasis);
- the presence of complications and concomitant pathologies that aggravate the patient's condition;
- the need to use medications that require regular monitoring of clinical and laboratory parameters.
Both local and systemic agents are used in the treatment of psoriasis.
Local therapy
This type of treatment is represented by ointments, gels, creams that are applied directly to the affected areas.
Topical glucocorticoids
These are hormonal drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect on the skin.In addition, hormones reduce itching, inhibit the immune response, reduce the spread of the inflammatory process and prevent the fusion of lesions.These medications are very effective, as shown by numerous studies.They can be used separately (for local forms) or in combination with other media.
This group includes flucinar, hydrocortisone, elocom, prednisolone, advantan, acriderm.Local glucocorticosteroids are available in the form of creams, ointments and lotions.
The disadvantage of these drugs is the risk of developing systemic (general) effects with prolonged use and large areas of exposure.These are the rules for the use of these medications:
- Use it only on the shortest courses possible.
- When infection occurs, preference should be given to glucocorticoids combined with an antibiotic or antifungal agent.
- Children should not apply hormones to the face, neck, or skin folds.
- It is better to start treating children with weak or moderately active drugs (prednisolone, hydrocortisone).
As a rule, hormonal agents are applied to psoriatic papules 1 or 2 times a day for up to 1 month.With prolonged use, adverse reactions may occur:
- burning, redness and itching;
- the appearance of acne;
- local infection;
- thinning, drying of the skin;
- reduction of pigmentation;
- stretch marks.
The skin of the face and groin often suffers from complications.
salicylic acid
It is used in combination with local glucocorticosteroids for significant peeling of the skin.Preparations containing salicylates (diprosalic, acriderm SK, elokom S) effectively remove exfoliated plaques and help restore the skin.
Vitamin therapy

Vitamin D is an effective treatment for local forms of psoriasis, as it reduces inflammation and excessive division of skin cells.Creams or ointments containing vitamin D3 (calcipotriol, daivonex, calcitriene) are applied to the plaques 1-2 times a day for about 2 months.It is not advisable to treat large areas of skin with them.It can be used together with glucocorticoid hormones.
Adverse reactions with local application of vitamin D3 are rare and are mainly represented by burning, redness and itching of the skin.In this case, I stop the treatment or use the ointment less frequently.In case of overdose, systemic manifestations of hypervitaminosis D are possible: decreased bone density and kidney stone formation.
Medicines in this group are not prescribed before starting UV therapy.
It is impossible to use externally drugs based on salicylic acid and vitamin D analogues simultaneously;this will lead to inactivation of the latter and significantly reduce the effectiveness of the therapy.
Zinc pyrithione
Preparations of this category (skin-cap, zinocap) are produced in the form of creams, sprays and shampoos.They are used not only to treat psoriasis, but also to prevent its relapses.The mechanism of action is antibacterial, antifungal activity and slowing down cell division.Medications can cause allergies, dryness, and skin irritation with repeated use.Therefore, the course of treatment should last no more than 1.5 months.
Systemic therapy
This treatment option involves the use of medications in tablet or injection form;They affect not only the integumentary tissues, but also the internal organs.Systemic treatment is used for moderate to severe psoriasis.
methotrexate
Medication from the group of cytostatics that stops cell division.It is prescribed for psoriatic arthritis, erythroderma, pustular and vulgaris psoriasis, if it does not respond to other types of therapy.
Methotrexate doses are selected individually and taken once or several times a week.Once the exacerbation subsides, the medication is continued at the lowest effective dose.The medication often causes side effects, so this treatment requires constant medical supervision.Possible adverse reactions:
- reduction in the number of all blood cells;
- appetite suppression, nausea, vomiting;
- the formation of ulcers and erosions in any part of the digestive system;
- damage to the liver and pancreas;
- headaches, drowsiness, seizures;
- visual disturbances;
- kidney dysfunction;
- suppression of germ cell formation processes;
- decreased libido;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- non-infectious pneumonia;
- allergic reactions.
The drug is discontinued if severe respiratory distress, cough, development of serious infectious diseases, anemia, or a significant increase in blood markers of kidney or liver failure occur.
cyclosporine
Medication that suppresses the function of the immune system.Taking into account the autoimmune nature of psoriasis, such therapy is justified;However, a general decrease in immunity often leads to infectious and oncological complications.Therefore, the drug is rarely used as maintenance therapy, but is prescribed only during exacerbations.Start taking cyclosporine with minimal doses, which are then increased until the desired result is obtained.
Adverse reactions to cyclosporine:
- impaired kidney function, swelling, increased blood pressure;
- toxic effect on the liver and pancreas, nausea, loose stools;
- formation of malignant tumors and lymphomas;
- decreased number of blood cells;
- muscle pain, cramps;
- headache;
- allergies.
The use of cyclosporine requires constant medical supervision, periodic blood tests and other necessary examinations.
Retinoids
Retinoids (acitretin, isotretinoin) are derivatives of vitamin A that have a normalizing effect on the processes of division and keratinization of skin cells.The course of treatment with such drugs is on average 2 months, the dosage is selected individually.When using retinoids, there is also a certain risk of unwanted reactions:
- drying of mucous membranes;
- peeling of the skin;
- fungal vulvovaginitis;
- hair loss, thinning, brittle nails;
- muscle and joint pain;
- inflammation of the liver, jaundice;
- nausea, stool disorders.
Despite the possible side effects, these medications are safer than previous options, especially considering that all of these complications are reversible and disappear some time after stopping the medication.Retinoids are not prescribed at the same time as methotrexate, as this increases the risk of damage to liver structures.
Monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies (infliximab, adalimumab, efalizumab) are genetically engineered biologics that are antibodies.They have the ability to suppress autoimmune processes and reduce inflammation.These medications are administered subcutaneously or intravenously no more than once a week.Its negative impact on the body is mainly associated with the suppression of the immune response:
- the addition of an infection from any location;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- allergic manifestations;
- headaches, dizziness;
- depression;
- nausea, vomiting;
- Joint and muscle pain.
The use of drugs from this category is possible in combination with methotrexate.
Systemic glucocorticoids
Systemic glucocorticoids (prednisolone, dexamethasone) are used exclusively in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis and acute generalized forms of the disease in injections and droppers.But even in these cases, the course of hormonal therapy should not be prolonged due to the risk of aggravating the process and the development of pustular forms.
Additional drug treatment
This group includes drugs necessary for the correction of concomitant conditions that aggravate the course of psoriasis and for the treatment of articular forms of the disease.
- Psychotropic drugs are used due to the high frequency of exacerbations of psoriasis against the background of an unstable nervous state.In particular, antidepressants (amitriptyline, fluoxetine, venlafaxine) and anxiolytics - tranquilizers (diazepam, phenazepam, buspirone) are prescribed.Antidepressants are usually prescribed for long-term depression and stress and are taken in long courses.Tranquilizers can be taken once, on demand, depending on external circumstances.This group of drugs suppresses anxiety, agitation, susceptibility to stress factors and normalizes sleep.However, it must be taken into account that medications also have their contraindications for use and adverse reactions, which do not always allow them to be taken simultaneously with the main therapy for psoriasis.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used in the complex therapy of psoriatic arthritis to reduce the inflammatory reaction, swelling and pain.These products are produced in the form of tablets, injectable solutions, gels and ointments for external use.Due to the negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract (ulcer formation), these drugs are prescribed for the shortest possible course.
- Antihistamines are occasionally used to reduce itchy skin.First (Tavegil, Suprastin), second (Fenistil, Claritin) or third (Zyrtec, Erius) prescription medications.The effectiveness of these medications is largely comparable;However, third-generation medications do not have such a common side effect of antihistamines as increased drowsiness.
Physiotherapy for psoriasis
Ultraviolet irradiation (UVR) involves exposure to radiation with a wavelength of 311-313 nm to the entire body or individual parts of it.This technique is not applicable for severe generalized forms of psoriasis and its summer variety, since it can only aggravate the process.
Selective phototherapy (PUVA therapy) is a type of ultraviolet radiation, but the wavelength used in this case is 310 to 340 nm.This physical therapy option, when used regularly, allows you to achieve long-term remission.One session can last up to 2 hours, and the recommended total number is 35. Dry skin may appear after the procedure, which will require the use of a moisturizer.PUVA therapy has several contraindications, such as renal failure, diabetes mellitus, and skin tumors.
Radiotherapy consists of treating the skin with gentle X-rays, which help effectively combat itching and the formation of new plaques.
Ultrasound treatment involves exposing the skin to ultrasonic waves, which have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, analgesic and antipruritic effects.A procedure lasts 15 minutes, does not cause discomfort and is well tolerated.A total course of 14 procedures is recommended.
Electrosleep indirectly affects the course of psoriasis, improving the patient's mental state.This manipulation causes a calming effect, improves sleep, increases resistance to stress and reduces excessive excitability of the nervous system.A session can last up to 1 hour, it is recommended to perform at least 10 procedures.
Psychotherapy
Numerous studies have shown the role of an unstable mental state in the development of psoriasis.Various types of stress, anxiety, fears and experiences often cause the appearance or exacerbation of psoriasis in people with a genetic predisposition.Psychotherapy is therefore important to prevent exacerbations and generally reduce the frequency of relapses.
During the session, the specialist talks with the patient, asks interesting questions and tries to establish the cause of psychological problems.Other sessions aim to stabilize the patient's emotional state.A psychotherapist can teach you how to cope with stress at work and at home, find an outlet for negative energy, and develop a positive attitude toward yourself and the world around you.
Therapeutic nutrition for psoriasis.
Patients with psoriasis are recommended:
- Drink more fluids: 7 to 10 glasses of still water or freshly squeezed juices a day.
- Eat more fruits and vegetables: grapes, nectarines, cherries, pineapples;beet, carrot, cucumber, cabbage, garlic, onion, dill, cumin.
- Do not forget about the protein component of the diet: chicken eggs, lean meats, nuts, legumes.
- There are only natural sweets: dried apricots, dates, raisins.
- Do not abuse citrus, tomatoes, red peppers, strawberries and honey.
- Avoid chocolate and high-fat whole milk.
- Do not drink alcohol, caffeine, spicy, salty or smoked foods.
Alternative methods to combat psoriasis.
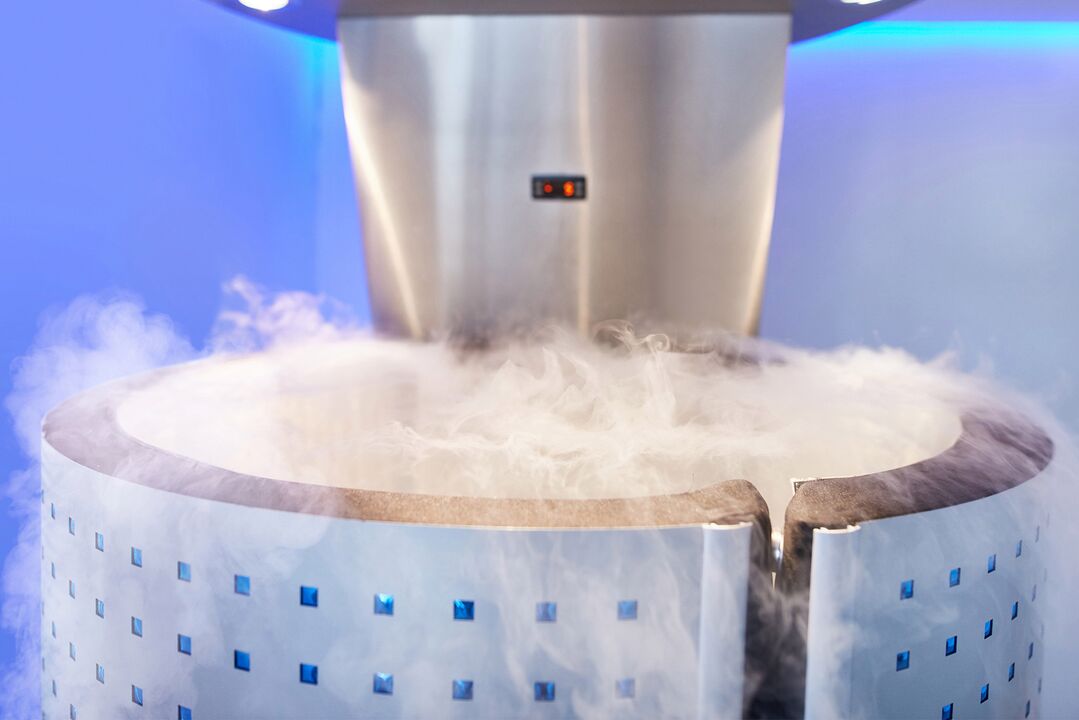

- Cryotherapy is the effect on the body of ultra-low temperatures, which can be local and general.The mechanism for improving the condition of psoriasis is the body's short-term stress response to cold.Against this background, a rapid narrowing and subsequent expansion of blood vessels occurs, which leads to an increase in blood flow and a decrease in inflammation.In addition, low temperatures drastically reduce the speed of nerve impulses and prevent the formation of new lesions.General cryotherapy is carried out using a special cryochamber, in which a person can stay no more than 3 minutes.The temperature in it is set in the range of -110 – -130°C.The entire course should not exceed 30 procedures.Local cryotherapy is carried out by exposing skin areas with psoriatic plaques to liquid nitrogen vapor (temperature -140 – -160°C).During the research, it was found that after a course of procedures, psoriatic papules pale, decrease in size, peeling and itching disappear.
- Hydrotherapy is widely used in sanatoriums with thermal waters.Garra rufa fish that live in these waters eat rough particles and scales from the surface of the skin, leaving healthy areas intact.
- Plasmapheresis is a rather complex process that involves removing blood from the patient's body, cleaning it from toxins, immune complexes, microorganisms and returning it to the general bloodstream.A special centrifuge is used to purify the blood.The positive effect of plasmapheresis in psoriasis is associated with the removal from the bloodstream of immune complexes that support the autoimmune reaction, degradation products formed as a result of chronic inflammation, as well as microorganisms and their toxins when secondary infection occurs.
- Mud therapy is an effective means of improving the health of patients with psoriasis.Due to the significant content of mineral salts, therapeutic mud suppresses the inflammatory process, promotes tissue regeneration and softens rough areas of the skin.Mud therapy allows you to achieve better results in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis.Before applying it to the skin, the mud is heated to 39°C, then a thin layer is spread over the areas covered with plaques and left to act for 30 minutes.At the end of the procedure, the dirt is washed off with warm water, and the skin is lubricated with a softening cream.
Traditional medicine recipes for psoriasis.
Home remedies for the treatment of psoriasis are divided into two groups: preparations for oral administration and external remedies.The first category includes:
- Celandine tincture.The herb of this plant can be found in the pharmacy.2 tablespoons l.The dried herb is poured with 500 ml of alcohol or vodka and left to brew for 10 to 14 days.The tincture is then filtered and 20 g are taken 3 times a day.
- Decoction of bay leaves.Place 15 bay leaves in 1 liter of boiling water and boil for about a quarter of an hour.Then filter, cool and drink 1 tbsp.l.3 times a day for 1 month.
- Dill seeds.2 tablespoons l.seeds, pour 1 glass of boiling water, let it brew for about three hours, filter, drink ½ glass 2 times a day.
- Flax seeds.1 tablespoon l.seeds, pour a glass of boiling water, stir, leave overnight, take in the morning, before breakfast.
Traditional external medicine for the treatment of psoriasis:
- Fish oil.Apply a thin layer on the papules and leave for half an hour, then wash with warm water.
- Linseed oil.Apply to the affected area up to 6 times a day.
- Egg ointment.Beat 2 chicken eggs, add 1 tbsp.l.sea buckthorn or sesame oil and 40 g of vinegar.Lubricate the plates 3 times a day.
- Propolis tar ointment.30 g of propolis and 50 g of tar are heated in a water bath and stirred.Apply to psoriatic rashes up to 4 times a day.
It should be noted that whatever alternative and popular methods you use in the treatment of psoriasis, they should not replace the main traditional therapy.All medications used for psoriasis must be strictly prescribed by a doctor.Under no circumstances should you self-medicate or change the dose and schedule of the drug at will.























